The Fire is a process of burning that produces heat, light and often smokes and flames.
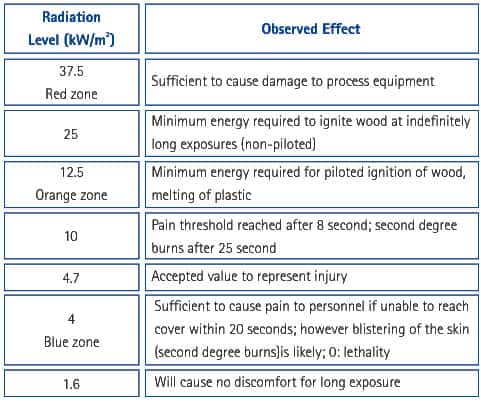
The effect of fire on the people takes the form of skin burn due to the exposure to thermal radiation. The severity of the burns depends upon the intensity of the heat and exposure time. In general terms the skin withstands heat energy of 10kw/m2 for approximately 8 seconds and that of 30kw/m2 for 0.4 seconds before pain is felt. The effect of various heat radiation levels is given in the table below.
Fire can takes several different forms i.e.
- Flash Fire
- Jet fire
- Pool Fire
- Secondary fire
Flash fire

A flash fire occurs when a cloud of flammable gas and air is ignited. The speed of burning is function of the concentration of the flammable component in the cloud and also the wind speed. Within a few second of ignition the flame spreads both upwind and downwind of the ignition source. Initially the flame is contained with in the cloud due to premixed burning of the regions within the flammable limits. Subsequently the flame extends in the form of a fire plume above the cloud. The downwind edge of the flame starts to move towards the spill point after consuming the flammable vapor downwind of the ignition source. The duration of this fire is very short and the damage is caused by thermal radiation and oxygen depletion.
Factors Influencing Human Behaviour
Jet Fire

A jet fire occurs when a flammable liquid or gas is ignited after its release from a pressurized, punctured vessel or pipe. The pressure of release generates a long flame, which is stable under most conditions. A flash flame may take the form of jet flame on reaching the spill point. The duration of the jet fire is determined by the release rate and the capacity of the source. Flame length increases directly with flow rate. Typically a pressurized release of 8kg/s would have a length of 35m. The cross winds also affects the flame length.
Pool fire

A pool fire occurs on ignition of an accumulation of liquid as a pool on the ground or on water or other liquid. A steadily burning fire is rapidly achieved as the flame vapour to sustain the fire is provided by evaporation of liquid by heat from the flames.

The maximum burning rate is function of the net heat of combustion and heat required for its vaporization. Generally heat radiation dominates the burning rate for lame greater than 1m diameters.
Secondary Fire
The secondary fire involves the combustion of flammable materials those are not directly concerned with the process, and some time present unnecessarily. For example:
- Stored raw material and products, including packaging materials;
- Combustible insulation of vessels, pipelines and electrical cables;
- Combustible building material and linings.
Protection is by elimination or segregation of combustible materials, use of incombustible materials of construction and insulation, and control of ignition sources. Careless or deliberate actions may defeat in-built precautions.

Jatin Dubey is a 26-year-old MBA student whose passion for storytelling and a deep love for literature have fueled his journey as an aspiring author. Born and raised in a small town, Jatin discovered the magic of words at a young age when he stumbled upon an old, dusty library tucked away in a forgotten corner of his neighborhood. As he delved into the world of books, he found solace and inspiration in the pages of classic novels and contemporary fiction.