What is a Mutual Fund: Investing can be a daunting task for many people, especially when it comes to understanding the different types of investments available. One such investment option that often confuses people is mutual funds. While mutual funds may seem complicated, they can be a simple and accessible way for investors to diversify their portfolios and benefit from professional management.
In this article, we will break down the basics of mutual funds, including what they are, how they work, and the different types of mutual funds available. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or new to investing, this guide will help you understand the ins and outs of mutual funds so you can make informed decisions about your investments. So, let’s dive into the world of mutual funds and discover what makes them a popular choice among investors.
What is a Mutual Fund?
Contents
- 1 What is a Mutual Fund?
- 2 Mutual Fund Overview
- 3 History of Mutual Funds
- 4 How Mutual Funds Work
- 5 Types of Mutual Funds
- 6 Advantages of Mutual Funds
- 7 Disadvantages of Mutual Funds
- 8 Conclusion
- 9 FAQs about Mutual Funds
- 9.1 What is a mutual fund?
- 9.2 How do mutual funds work?
- 9.3 What are the benefits of investing in mutual funds?
- 9.4 What are the different types of mutual funds?
- 9.5 What are the fees associated with mutual funds?
- 9.6 How do I invest in a mutual fund?
- 9.7 Are mutual funds a good investment option for beginners?
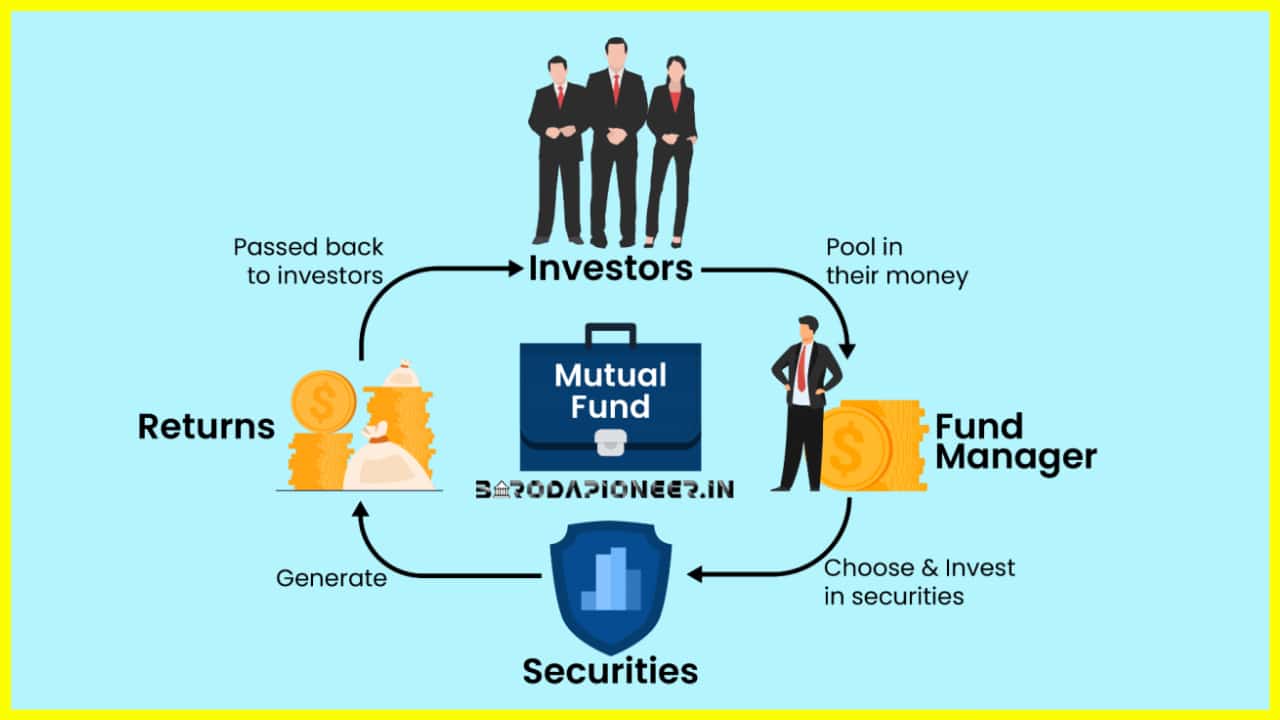
A mutual fund is a type of investment vehicle that pools money from a group of investors to purchase a portfolio of securities, such as stocks, bonds, and other assets. The fund is managed by professional investment managers who are responsible for making investment decisions on behalf of the fund’s investors. Mutual funds provide investors with a way to diversify their investments, reduce their risk, and access a range of investment opportunities that they may not have otherwise.
Mutual Fund Overview
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | A type of investment where a large group of people pool their money together to invest in a variety of assets, such as stocks, bonds, or other securities. The mutual fund is managed by an investment professional who makes decisions about what assets to invest in based on the fund’s objectives. |
| How it Works | Investors buy shares in the mutual fund, and the value of the shares is based on the performance of the underlying assets in the fund. The mutual fund manager invests the money from the shareholders in a variety of assets, diversifying the portfolio to reduce risk. Investors receive a portion of the returns based on the performance of the assets in the fund. |
| Benefits | Professional management, diversification, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness. Investors can benefit from the collective power of a large group of investors and access a range of investment opportunities they may not have been able to access on their own. |
| Types | Index funds, bond funds, equity funds, sector funds, specialty funds, international funds, and alternative funds. Each type of fund has its own investment strategy and objectives. |
| Fees | Mutual funds typically have fees associated with them, such as management fees, expenses, and sales charges. It’s important to be aware of the fees and how they can impact your overall return on investment. |
| Investing | Mutual funds can be purchased through a variety of channels, including financial advisors, brokerage firms, and online platforms. It’s important to do your research and understand the fees, investment strategy, and objectives of the mutual fund before investing. |
| Suitability for Beginners | Mutual funds can be a good investment option for beginners because they offer diversification, professional management, and accessibility. However, it’s important to carefully consider your investment goals and risk tolerance before investing in a mutual fund. |
History of Mutual Funds
The history of mutual funds can be traced back to the 18th century, when Dutch merchant Adriaan van Ketwich founded the first investment trust in Amsterdam in 1774. However, the modern mutual fund industry as we know it today began in the United States in the early 20th century.
The first modern mutual fund, the Massachusetts Investors Trust, was launched in 1924 by a group of investment professionals led by MIT economist Edwin F. Gay. The fund was designed to provide small investors with access to a diversified portfolio of stocks, which were otherwise out of reach for most individuals at the time.
The mutual fund industry continued to grow throughout the 20th century, and by the 1990s, mutual funds had become one of the most popular investment vehicles for individual investors. Today, there are thousands of mutual funds available to investors, covering a wide range of investment strategies and asset classes.
Get here : Free Job Alert 2024
How Mutual Funds Work
When you invest in a mutual fund, you are buying shares in the fund, just like you would buy shares in a company. The value of your shares is determined by the net asset value (NAV) of the fund, which is calculated by dividing the total value of the fund’s assets by the number of shares outstanding.
The NAV of a mutual fund is calculated at the end of each trading day, based on the closing prices of the securities held in the fund’s portfolio. This means that the value of your shares will fluctuate with the performance of the fund’s underlying assets.
Mutual funds are typically structured as open-end funds, which means that they are continuously buying and selling securities as investors buy and sell shares of the fund. This allows investors to buy and sell shares of the fund at any time, and ensures that the fund’s assets are always fully invested.
Types of Mutual Funds
There are many different types of mutual funds, each with its own investment objective and strategy. Here are some of the most common types of mutual funds:
-
Equity Funds
Equity funds invest primarily in stocks, and are designed to provide investors with long-term capital appreciation. Equity funds can be further divided into sub-categories based on their investment style, such as growth funds, value funds, and sector funds.
-
Fixed Income Funds
Fixed income funds invest primarily in bonds, and are designed to provide investors with regular income and preservation of capital. Fixed income funds can be further divided into sub-categories based on the type of bonds they invest in, such as government bonds, corporate bonds, and high-yield bonds.
-
Balanced Funds
Balanced funds invest in a mix of stocks and bonds, and are designed to provide investors with a balanced portfolio of both growth and income. Balanced funds can be further divided into sub-categories based on the specific allocation of stocks and bonds, such as 60/40 funds or 50/50 funds.
-
Money Market Funds
Money market funds invest in short-term debt securities, such as Treasury bills and commercial paper. Money market funds are designed to provide investors with a low-risk, low-return investment option, and are often used as a place to park cash in between other investments.
-
Index Funds
Index funds are designed to track the performance of a specific market index, such as the S&P 500 or the Dow Jones Industrial Average.
When will Mirzapur Season 3 Release in 2024?
-
Specialty Funds
Specialty funds invest in a specific industry or sector, such as technology or healthcare. These funds are designed to provide investors with exposure to a particular market segment, and may offer the potential for higher returns but also higher risk.
-
International Funds
International funds invest in stocks and bonds outside of the investor’s home country, and are designed to provide investors with exposure to global markets. International funds can be further divided into sub-categories based on the region or country they invest in, such as emerging markets or developed markets.
-
Alternative Funds
Alternative funds invest in assets that are not typically found in traditional mutual funds, such as commodities, real estate, or private equity. These funds are designed to provide investors with exposure to non-traditional assets and strategies, and may offer the potential for higher returns but also higher risk.
check Sarkari Result
Advantages of Mutual Funds
- Diversification: Mutual funds provide investors with a way to diversify their investments across a wide range of assets, which can help to reduce risk.
- Professional management: Mutual funds are managed by professional investment managers who have the expertise to make investment decisions on behalf of the fund’s investors.
- Accessibility: Mutual funds are widely available and can be purchased through a variety of channels, including financial advisors, brokerage firms, and online platforms.
- Liquidity: Mutual funds can be bought and sold on a daily basis, which makes them a highly liquid investment option.
- Cost-effectiveness: Mutual funds typically have lower fees than other types of investments, such as actively managed funds or individual securities.
Disadvantages of Mutual Funds
- Fees: While mutual funds typically have lower fees than other types of investments, they still have fees associated with them, such as management fees and expenses.
- Lack of control: When you invest in a mutual fund, you are entrusting your money to a professional manager, which means you have less control over the investment decisions being made.
- Market risk: Mutual funds are subject to market risk, which means that the value of your investment can fluctuate based on the performance of the fund’s underlying assets.
- Tax implications: Mutual fund distributions can be subject to taxes, which can affect your overall return on investment.
Conclusion
Mutual funds are a popular investment vehicle that provide investors with a way to access a wide range of assets and strategies, while also benefiting from professional management and diversification. However, investors should be aware of the fees, lack of control, market risk, and tax implications associated with mutual funds, and should carefully consider their investment goals and risk tolerance before investing.
FAQs about Mutual Funds
What is a mutual fund?
A mutual fund is a type of investment where a large group of people pool their money together to invest in a variety of assets, such as stocks, bonds, or other securities. The mutual fund is managed by an investment professional who makes decisions about what assets to invest in based on the fund's objectives.
How do mutual funds work?
When you invest in a mutual fund, you buy shares in the fund. The value of the shares is based on the performance of the underlying assets in the fund. The mutual fund manager invests the money from the shareholders in a variety of assets, diversifying the portfolio to reduce risk. Investors receive a portion of the returns based on the performance of the assets in the fund.
What are the benefits of investing in mutual funds?
Mutual funds offer several benefits, including professional management, diversification, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness. Investors can benefit from the collective power of a large group of investors and access a range of investment opportunities they may not have been able to access on their own.
What are the different types of mutual funds?
There are several types of mutual funds, including index funds, bond funds, equity funds, sector funds, specialty funds, international funds, and alternative funds. Each type of fund has its own investment strategy and objectives.
What are the fees associated with mutual funds?
Mutual funds typically have fees associated with them, such as management fees, expenses, and sales charges. It's important to be aware of the fees and how they can impact your overall return on investment.
How do I invest in a mutual fund?
Mutual funds can be purchased through a variety of channels, including financial advisors, brokerage firms, and online platforms. It's important to do your research and understand the fees, investment strategy, and objectives of the mutual fund before investing.
Are mutual funds a good investment option for beginners?
Mutual funds can be a good investment option for beginners because they offer diversification, professional management, and accessibility. However, it's important to carefully consider your investment goals and risk tolerance before investing in a mutual fund.

Jatin Dubey is a 26-year-old MBA student whose passion for storytelling and a deep love for literature have fueled his journey as an aspiring author. Born and raised in a small town, Jatin discovered the magic of words at a young age when he stumbled upon an old, dusty library tucked away in a forgotten corner of his neighborhood. As he delved into the world of books, he found solace and inspiration in the pages of classic novels and contemporary fiction.